Installing Odoo
by Bill Jellesma2021-09-12 17:00:00

Updates
- 2022-02-27 - Update database creation
Odoo is an Open Source Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system making it easier to manage inventory and facilitate sales and purchase orders, among other features. What makes Odoo nicer to work with than other ERP systems is the app store like way enabling you to install features that you need and leave out features that you don't need. These features that you can install are referred to as modules. Like the app store for Iphone and Android, you can even choose to write your own if you desire additional functionality.
While Odoo opens up a world of possibilities, the first step is to install the base Odoo (Selecting to download it from source) system. The base Odoo System also comes with several built in modules.
Installing
In the following steps, we'll be running Odoo from source. I find this to be a better approach than a packaged installation from a development point of view because you'll be able to create custom modules if you wish. I'm using Linux Mint to install Odoo so these commands will work well for a Debian based distribution like Linux Mint or Ubuntu. If you're using another distribution like Fedora, you should be able to use yum or your distribution's package manager to install packages like sudo yum update.
Install Githttps://billjellesmacoding.netlify.app/blog/20210912_odoo_instally so that we can run Odoo from source.
Use Git to clone the odoo community repo
Navigate in the terminal to the directory where you would like Odoo to reside and clone the repository with git clone https://github.com/odoo/odoo.git. Even if you're planning to use the enterprise version of Odoo, you will still need to clone and run the Odoo community repo. This is necessary because you'll use the odoo-bin file that comes in the community repo to run the Odoo server.
Note that the enterprise version of Odoo is just another addons folder that we can run on our command line.
- Install Python 3
Odoo uses Python 3 to run its server. Your linux distribution most likely comes with python 2 installed so you will also need to install python 3. Update your software repository using sudo apt-get update and install python with sudo apt-get install python 3.9. Note that 3.9 is the current version as of September 2021. Because installing python 3 will lead to you having two python interpreters, you may need to use python3 on the command line as opposed to python as would probably be the case on Windows. You can easily verify the python installations by typing python3 --version and python --version.
- Install PostGres
sudo apt-get install postgresql-{version} postgresql-client-{version} where {version} is the most recent version of postgres released should do the trick to install PostGres. PostGres is the database used by Odoo.
- Create a new PostGres User
First, switch to the postgres user to create the new database user with sudo su - postgres. The easiest and quickest way that I've found to use PostGres is with the current user so create the user with createuser --createdb --username postgres --no-createrole --pwprompt {user} where {user} is the name of the currently logged in user.
Note in the above command that even though postgres is being used as the username, this means that we're connecting as postgres, we're still creating a new user.
- Install the required Linux dependencies
Using a debian based distribution, we can install the required dependencies with
sudo apt install python3-dev libxml2-dev libxslt1-dev libldap2-dev libsasl2-dev \
libtiff5-dev libjpeg8-dev libopenjp2-7-dev zlib1g-dev libfreetype6-dev \
liblcms2-dev libwebp-dev libharfbuzz-dev libfribidi-dev libxcb1-dev libpq-dev python3-pypdf2 python3-decorator python3-polib \
python3-html2text python3-docutils python3-libsassThese will be the linux packages required for installation.
- Install the required python dependencies
In addition to the Linux dependencies, we'll also need to install dependencies for python in order to properly run the program. In the same directory with the requirements.txt, run the following commands
pip3 install setuptools wheel
pip3 install -r requirements.txt- Start the server and setup the database
Once you've started the server with python .\odoo-bin and gone to http://localhost:8069/web/database/selector, you should be presented with a screen asking you to choose existing databases or to manage your databases and setup a new one.
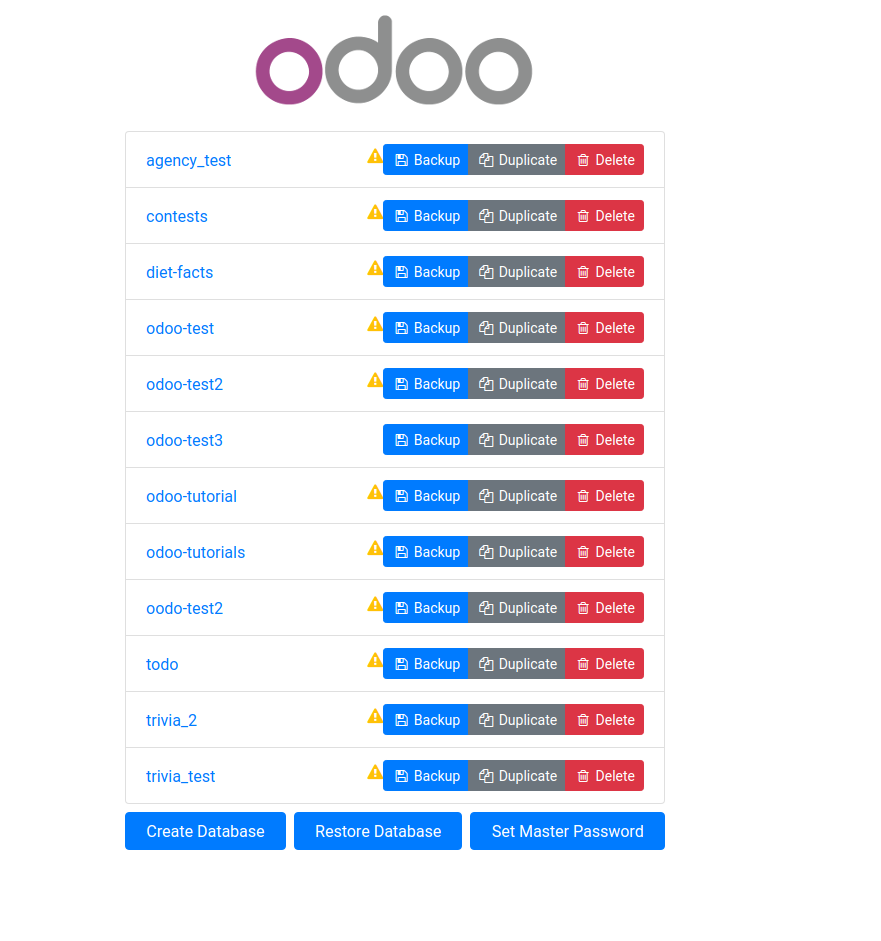
On this screen, you should create a database.
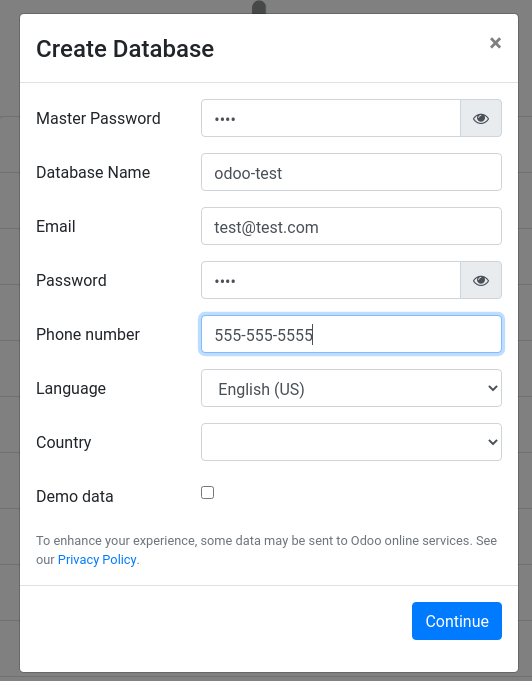
If you encounter an access denied error, it may be that there already is a master password.
You can set a master password while starting the odoo server by appending admin_passwd to your conf file. Also, make sure to set your database user credentials in the below run.conf file. If the postgres user that you created above in "Create a new PostGres User" is named user, use this username for db_user. A detailed explanation of the conf file is in the next section. But the file would look like the following
[options]
addons=~/path/odoo/addons
database=odoo-test
admin_passwd=test
db_host=localhost
db_maxconn=64
db_user=user
db_password=password
db_port=5432All Set
You can now run the Odoo server by navigating to the Odoo directory with python3 ./odoo-bin --addons addons --database {database} where {database} is the database that you've setup previously. Optionally, you can create a configuration file to run your installation giving you an easier command to run. The structure of the configuration for our purposes would be
[options]
addons=[addons folder]
database=[database]Where the [addons folder] is the path to our addons and [database] is the name of our database.
Let's call our file run.conf
[options]
addons=~/path/odoo/addons
database=odoo-testWe can now run python3 ./odoo-bin -c run.conf. This has the advantages of not needing to remember configuration parameters, making the environment easier to share with teammates, and making it easier to change configuration parameters by editing a file rather than the command line.
Odoo should now be live and we can navigate to this in a browser by going to http://localhost:8069.
Logging in
We'll now be at the login screen. However, we don't have a username and password that we can use. Or do we? Every default installation comes with an admin account which is user ID 2. We can simply use psql to reset this password.
On the command line use psql odoo-test (assuming the name of your database is odoo-test) to go to a postgres prompt where we can begin executing commands against the database. With this prompt, we can execute the command UPDATE res_users SET password = "{password}" WHERE id=2 where {password} is the password that you'd like to set the admin's password to.
Back at the login screen, we can now login with admin and our chosen password.
Clean Install
Although there are other installation methods such as a packaged installation or creating a database through the browser, this installation offers you a clean Odoo. The modules that you will see on your home screen are Apps (app store) and Settings (system settings). For Development purposes, a clean installation is extremely useful so that we can know exactly what dependencies and extra settings that we'll need.